CP-template-AND-interesting-problems
JourneyProblem Link
problem simplified:
Given a tree. The length of each edge is 1. You start form node 1 and each time you choose any adjacent node and go there(untill you go to a leaf). You can’t visit an edge twice. Find the expected length of your visited path.
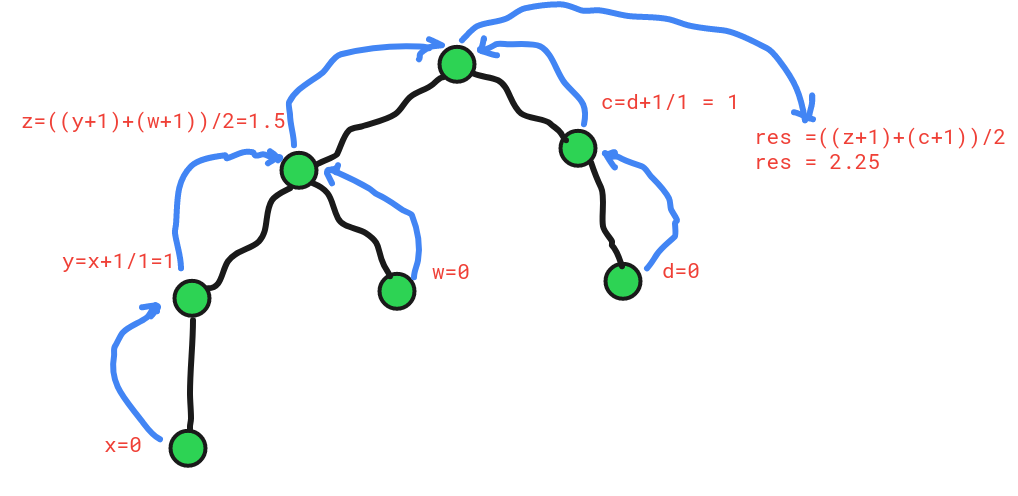
The figure below shows how the dfs function returning the values in each step(return values are in red color) </br>
observations
- Given graph is a tree
-
Let you are in node x. from there you have
nadjacent node you can go each having expected length: E1, E2,…En. then Expected value form node x is-`Ex = { (E1+1) + (E2+1) + ....+(En+1) } / n`
Solution Code(C++)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define lli long long int
#define lf long double
vector<lli>grp[100006];
lf dfs(lli src, lli p){
lf expected = 0;
lf path = 0;
for(int i=0; i<grp[src].size(); i++){
int nxt = grp[src][i];
if(nxt != p){
expected += 1+dfs(nxt, src);
path++;
}
}
if(path == 0) return 0;
return (expected / path);
}
int main() {
lli n; cin>>n;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++){
lli u, v; cin>>u>>v;
grp[u].push_back(v);
grp[v].push_back(u);
}
cout << fixed << setprecision(15);
cout<<dfs(1,-1);
}